~~ODT~~
BASIC-256 Syntax Reference
Σύνταξη προγράμματος
Τα προγράμματα στην BASIC-256 αποτελούνται από ένα σύνολο εντολών, χωρισμένων σε σειρές, οι οποίες εκτελούνται διαδοχικά.
Αριθμοί
Ως αριθμοί θεωρούνται οποιοιδήποτε αριθμητικοί χαρακτήρες, που μπορούν προαιρετικά να έχουν ένα πλην για υπόδειξη αρνητικών αριθμών ή/και μια τελεία ακολουθούμενη από περισσότερους αριθμητικούς χαρακτήρες για υπόδειξη δεκαδικών αριθμών. Κάποια παραδείγματα δεκαδικών αριθμών είναι:
| Δεκαδικοί αριθμοί |
|---|
| 10 |
| -234.567 |
| 56.87 |
| 0.0123 |
Πολύ μεγάλοι ή πολύ μικροί αριθμοί μπορούν επίσης να γραφούν στην επιστημονική μορφή (προστέθηκε στην έκδοση 0.9.9.46). http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scientific_notation
| Επιστημονική μορφή | Δεκαδικός αριθμός |
|---|---|
| 2e0 | 2 |
| 3e2 | 300 |
| 1.234e10 | 12340000000 |
| -5.3e4 | -53000 |
| 2e-1 | 0.2 |
| 5.12e-9 | 0.00000000512 |
Θετικοί ακέραιοι αριθμοί μπορούν επίσης να αναπαρασταθούν στο δυαδικό (βάση 2), οκταδικό (βάση 8), και δεκαεξαδικό (βάση 16) σύστημα. Γράψε μπροστά 0b για δυαδικούς (0b1110 = 14), 0o για οκταδικούς (0o177 = 127), και 0x για δεκαεξαδικούς (0xff = 255).
Συμβολοσειρές
Συμβολοσειρές είναι κανένας ή περισσότεροι χαρακτήρες μέσα σε διπλά εισαγωγικά(“).
Μεταβλητές
Τα ονόματα των μεταβλητών που περιέχουν αριθμούς πρέπει να ξεκινούν με ένα γράμμα, και έπειτα μπορούν να ακολουθηθούν από οποιονδήποτε αριθμό γραμμάτων ή αριθμητικών χαρακτήρων. Η ύπαρξη κεφαλαίων ή πεζών γράμματων έχει σημασία. Οι αριθμητικές μεταβλητές μπορούν να χρησιμοποιηθούν στην θέση αριθμών.
Η ονομασία των μεταβλητών που περιέχουν συμβολοσειρές ακολουθεί τους ίδιους κανόνες με τις αριθμητικές μεταβλητές, άλλα το όνομα πρέπει επιπλέον να τελειώνει με το σήμα του δολλαρίου ($). Μπορούν να χρησιμοποιηθούν αντί συμβολοσειρών.
Όταν εκχωρείς έναν αριθμό σε μια αλφαριθμητική μεταβλητή ή προσθέτεις έναν αριθμό σε μια συμβολοσειρά (συνένωση), τότε ο αριθμός αυτόματα μετατρέπεται σε συμβολοσειρά προτού ολοκληρωθεί η πράξη. Μια συμβολοσειρά δεν μπορεί να εκχωρηθεί σε μια αριθμητική μεταβλητή πριν την μετατροπή του τύπου της με χρήση των συναρτήσεων Int ή Float.
| Εκχωρισμός μεταβλητών | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Τελεστής | Περιγραφή | Παράδειγμα | Σχόλια |
| = | Εκχώρηση αριθμού σε αριθμητική μεταβλητή | a = 9 | |
| = | Εκχώρηση συμβολοσειράς σε αλφαριθμητική μεταβλητή | z$ = “Hola.” | |
| = | Εκχώρηση αριθμού σε αλφαριθμητική μεταβλητή | q$ = 9.9 | |
| += | Πρόσθεση με αριθμητική μεταβλητή | a += 7 | Ίδιο με a = a + 7 1 |
| += | Συνένωση με αλφαριθμητική μεταβλητή | f$ += “.” | Ίδιο με f$ = f$ + “.” 1 |
| -= | Αφαίρεση από αριθμητική μεταβλητή | a -= 9 | Ίδιο με a = a - 9 1 |
| *= | Πολλαπλασιασμός αριθμητικής μεταβλητής με | a *= 2 | Ίδιο με a = a * 2 1 |
| /= | Διαίρεση αριθμητικής μεταβλητής με | a /= 8 | Ίδιο με a = a / 8 1 |
1 προστέθηκε με την έκδοση 0.9.9.10
Πίνακες
Οι πίνακες δημιουργούνται με χρήση της εντολής DIM και αναμεγεθύνονται με την εντολή Redim. Μπορούν να περιέχουν αριθμούς ή συμβολοσειρές. Η προσπέλαση συγκεκριμένων στοιχείων ενός πίνακα επιτυγχάνεται γράφοντας το όνομα του πίνακα, ακολουθούμενο από αγκύλες που εσωκλείουν την θέση του στοιχείου, ξεκινώντας από το μηδέν. Οι πίνακες μπορούν να είναι και δισδιάστατοι, οπότε χρησιμοποιούμε δύο αριθμούς μέσα σε αγκύλες για την προσπέλαση στοιχείων.
Τα μεγέθη των πινάκων μπορούν να εξαχθούν γράφοντας [?] [?,] και [,?] στο τέλος του ονόματος του πίνακα.
Παράδειγμα
print pinakas[4]
θα απεικονίσει στην οθόνη το πέμπτο στοιχείο του 'pinakas'
Ακαθόριστοι πίνακες
Ένας ακαθόριστος πίνακας είναι ένα σύνολο αριθμών ή συμβολοσειρών, χωρισμένων με κόμματα, μέσα σε άγκιστρα {}. Μπορεί να χρησιμοποιηθεί για την άμεση εκχώρηση μιας ομάδας τιμών σε έναν πίνακα. Εάν ο ακαθόριστος πίνακας είναι μακρύτερος από τον εκχωρητέο πίνακα, τότε ο τελευταίος θα αναμεγεθυνθεί (Redim) αυτόματα.
Ακαθόριστοι πίνακες μπορούν επίσης να χρησιμοποιηθούν στην θέση κανονικών πινάκων στις εντολές Poly, Sound, και Stamp.
Παράδειγμα
dim myarray(4)
myarray = {1, 2, 3, 4}
dim words$(1)
words$ = {"how","now","brown","cow"}
for n = 0 to words$[?]-1
print words$[n]
next n
Τελεστές
Οι τελεστές +, -, *, /, και ^ χρησιμοποιούνται για πρόσθεση, αφαίρεση, πολλαπλασιασμό, διαίρεση και ύψωση σε δύναμη δεκαδικών και ακεραίων αριθμών. Έγκυροι τελεστέοι είναι αριθμοί ή/και αριθμητικές μεταβλητές.
Οι τελεστές %, \, &, |, και ~ χρησιμοποιούνται για τον υπολογισμό υπολοίπου, ακέραιας διαίρεσης, δυαδικής σύζευξης, δυαδικής διάζευξης, και δυαδικής άρνησης ακεραίων αριθμών. Οι δεκαδικοί αριθμοί θα μετατρέπονται σε ακέραιους πριν τον υπολογισμό.
Ο τελεστής = χρησιμοποιείται και για εκχωρισμό μεταβλητών, άλλα και για έλεγχο ισότητας. Ο τελεστής + μπορεί επίσης να χρησιμοποιήθεί για την συνένωση οποιουδήποτε συνδυασμού συμβολοσειρών και αλφαριθμητικών μεταβλητών. Ο τελεστής : διαχωρίζει εντολές που βρίσκονται πολλές μαζί σε μια γραμμή. Ο τελεστής ; παρεμποδίζει την αυτόματη αλλαγή σειράς της εντολής PRINT. Ο τελεστής # είναι μια συντομογραφία της εντολής Rem, και μπορεί να χρησιμοποιηθεί αντί αυτής.
| Αριθμητικοί τελεστές | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Τελεστής | Όνομα | Παράδειγμα | Σχόλια |
| + | Προσθεση | a + b | Προσθέτει δύο αριθμούς |
| - | Αφαίρεση | a - b | Αφαιρεί δύο αριθμούς |
| * | Πολλαπλασιασμός | a * b | |
| / | Διαίρεση | a / b | Επιστρέφει των δεκαδικό αριθμό φορών που το b χωράει στο a. |
| \ | Ακέραια διαίρεση | a \ b | Επιστρέφει τον ακέραιο αριθμό φορών που το b χωράει στο a. |
| % | Modulo | a % b | Επιστρέφει το υπόλοιπο της ακέραιας διαίρεσης των a και b. |
| ++ | Αυξητικό πρόθημα | ++a | Αυξάνει (κατά ένα) την μεταβλητή και επιστρέφει την τιμή της μετά την αύξηση. (μπορεί να εφαρμοστεί ΜΟΝΟ σε αριθμητικές μεταβλητές ή δείκτες πινάκων) 1 |
| ++ | Αυξητικό επίθημα | a++ | Επιστρέφει την τιμή της μεταβλητής και μετά την αυξάνει κατά ένα για την επόμενη φορά που αυτή θα προσπελαστεί. (μπορεί να εφαρμοστεί ΜΟΝΟ σε αριθμητικές μεταβλητές ή δείκτες πινάκων) 1 |
| – | Μειωτικό πρόθημα | –a | Μειώνει (κατά ένα) την μεταβλητή και επιστρέφει την τιμή της μετά την μείωση. (μπορεί να εφαρμοστεί ΜΟΝΟ σε αριθμητικές μεταβλητές ή δείκτες πινάκων) 1 |
| – | Μειωτικό επίθημα | a– | Επιστρέφει την τιμή της μεταβλητής και μετά την μειώνει κατά ένα για την επόμενη φορά που αυτή θα προσπελαστεί. (μπορεί να εφαρμοστεί ΜΟΝΟ σε αριθμητικές μεταβλητές ή δείκτες πινάκων) 1 |
| Τελεστές σύγκρισης | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Τελεστής | Όνομα | Παράδειγμα | Σχόλια |
| = | Ίσο | a = b | Επιστρέφει αλήθεια (true) εάν δύο τιμές είναι ίσες |
| < | Μικρότερο από | a < b | |
| > | Μεγαλύτερο από | a > b | |
| <= | Μικρότερο ή ίσο | a <= b | |
| >= | Μεγαλύτερο ή ίσο | a >= b | |
| <> | Άνισο | a <> b | |
| Λογικοί τελεστές | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Τελεστής | Όνομα | Παράδειγμα | Σχόλια |
| NOT | Λογική άρνηση | NOT a | |
| AND | Λογική σύζευξη | a AND b | |
| OR | Λογική διάζευξη | a OR b | |
| XOR | Λογική απoκλειστική διάζευξη | a XOR b | |
| Δυαδικοί τελεστές | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Τελεστής | Όνομα | Παράδειγμα | Σχόλια |
| ~ | Δυαδική άρνηση | ~a | |
| & | Δυαδική σύζευξη | a & b | |
| | | Δυαδική διάζευξη | a | b | Επιστρέφει τα δυαδικά ψηφία της διάζευξης των ακεραίων a και b. |
| Τελεστές συμβολοσειρών | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Τελεστής | Όνομα | Παράδειγμα | Σχόλια |
| + | Συνένωση | a$ + b$ | Επιθέτει το b$ στο τέλος του a$. |
| Προτεραιότητα τελεστών | ||
|---|---|---|
| Επίπεδο | Τελεστές | Κατηγορία/Περιγραφή |
| 1 | ( ) | Ομαδοποίηση |
| 2 | ^ | Έκθεση |
| 3 | - ~ | Μοναδιαίο πλήν και δυαδική άρνηση (NOT) |
| 4 | * / \ | Πολλαπλασιασμός και διαίρεση |
| 5 | % | Ακέραιο υπόλοιπο (Mod) |
| 6 | + - | Πρόσθεση, συνένωση, και αφαίρεση |
| 7 | & | | Δυαδική σύζευξη και διάζευξη |
| 8 | < ⇐ > >= = <> | Σύγκριση (αριθμών και συμβολοσειρών) |
| 9 | NOT | Μοναδιαία άρνηση |
| 10 | AND | Λογική σύζευξη |
| 11 | OR | Λογική διάζευξη |
| 12 | XOR | Λογική αποκλειστική διάζευξη |
1 εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση 0.9.9.10
Statements and Functions - Alphabetic
Abs
Format
abs ( expression )
Description
Returns the absolute value of a numeric expression.
Example
print abs(-45) print abs(6.45)
will print
45 6.45
Acos
Format
acos ( expression )
Description
Computes the arc-cosine of expression.Angles are expressed in radians (0 to 2pi).
See Also
Asc
Format
asc ( expression )
Description
Converts the first character in a string expression to an integer representing it's ASCII value.
| Asc | Chr | Asc | Chr | Asc | Chr | Asc | Chr | Asc | Chr | Asc | Chr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32 | SPACE | 48 | 0 | 64 | @ | 80 | P | 96 | ` | 112 | p |
| 33 | ! | 49 | 1 | 65 | A | 81 | Q | 97 | a | 113 | q |
| 34 | “ | 50 | 2 | 66 | B | 82 | R | 98 | b | 114 | r |
| 35 | # | 51 | 3 | 67 | C | 83 | S | 99 | c | 115 | s |
| 36 | $ | 52 | 4 | 68 | D | 84 | T | 100 | d | 116 | t |
| 37 | % | 53 | 5 | 69 | E | 85 | U | 101 | e | 117 | u |
| 38 | & | 54 | 6 | 70 | F | 86 | V | 102 | f | 118 | v |
| 39 | ' | 55 | 7 | 71 | G | 87 | W | 103 | g | 119 | w |
| 40 | ( | 56 | 8 | 72 | H | 88 | X | 104 | h | 120 | x |
| 41 | ) | 57 | 9 | 73 | I | 89 | Y | 105 | i | 121 | y |
| 42 | * | 58 | : | 74 | J | 90 | Z | 106 | j | 122 | z |
| 43 | + | 59 | ; | 75 | K | 91 | [ | 107 | k | 123 | { |
| 44 | , | 60 | < | 76 | L | 92 | \ | 108 | l | 124 | | |
| 45 | - | 61 | = | 77 | M | 93 | ] | 109 | m | 125 | } |
| 46 | . | 62 | > | 78 | N | 94 | ^ | 110 | n | 126 | ~ |
| 47 | / | 63 | ? | 79 | O | 95 | _ | 111 | o | 127 | |
See Also
Example
print asc("A")
print asc("blue")
will print
65 98
New To Version
0.9.4
Asin
Format
asin ( expression )
Description
Computes the arc-sine of expression. Angles are expressed in radians (0 to 2pi).
See Also
Atan
Format
atan ( expression )
Description
Computes the arc-tangent of expression. Angles are expressed in radians (0 to 2pi).
See Also
Ceil
Format
ceil ( expression )
Description
Returns the lowest integer that is greater than or equal to expression.
See Also
Example
print ceil(9.1) print ceil(-5.4)
will print
10 -5
Changedir
Σύνταξη
changedir Διαδρομή Αρχείου
changedir ( Διαδρομή Αρχείου )
Περιγραφή
Αλλάζει την τρέχουσα διαδρομή αρχείου σε αυτήν που καθορίζει η Διαδρομή Αρχείου. Σε όλα τα λειτουργικά συστήματα (συμπεριλαμβανομένων των Windows) μια δεξιά κάθετος (/) διαχωρίζει τους φακέλους μιας διαδρομής.
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.6r
Chr
Format
chr ( expression )
Description
Converts the integer expression into a single character string expression with the ASCII value of the number. See asc for a complete ASCII character conversion chart.
See Also
Example
print chr(66)+chr(111)+chr(111)+chr(33)
will print
Boo!
New To Version
0.9.4
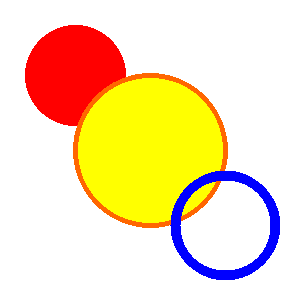
Circle
Σύνταξη
circle x,y,r
circle ( x,y,r )
Περιγραφή
Ζωγραφίζει έναν κύκλο με κέντρο x,y και ακτίνα r χρησιμοποιώντας τα τρέχοντα χρώματα πινέλου και στυλού.
Παράδειγμα
clg color red circle 75,75,50 penwidth 5 color orange, yellow circle 150,150,75 penwidth 10 color blue, clear circle 225,225,50
Δες επίσης
Clickb
Format
clickb
clickb ( )
Description
Returns the buttons that the user last clicked on the mouse (if over the graphic output). Returns 0 if no click has been recorded. If multiple buttons have been pressed the value is the sum of the values for all pressed buttons.
| Return Values | |
|---|---|
| Value | Mouse Button Pressed |
| 0 | None |
| 1 | Left |
| 2 | Right |
| 4 | Center |
See Also
Example
# clear any prior mouse click
clickclear
# wait for the user to click the mouse
print "click mouse on the graphics output"
while clickb = 0
pause .01
endwhile
# show where the user clicked
print "The user clicked at (" + clickx + "," + clicky + ")"
New To Version
0.9.4d
Clickclear
Format
clickclear
clickclear ( )
Description
Sets ClickB, Clickx, and Clicky to zero so that we can easily tell when the next mouse click is recorded.
See Also
Example
See sample program on Clickb.
New To Version
0.9.4d
Clickx
Format
clickx
clickx ( )
Description
Returns the mouse x location of the mouse pointer over the graphic output last time the user clicked a mouse button.
See Also
Example
See sample program on Clickb.
New To Version
0.9.4d
Clicky
Format
clicky
clicky ( )
Description
Returns the mouse y location of the mouse pointer over the graphic output last time the user clicked a mouse button.
See Also
Example
See sample program on Clickb.
New To Version
0.9.4d
Clg
Format
clg
Description
Clears the graphics output window.
Close
Σύνταξη
close
close ( )
close ΑριθμόςΑρχείου
close ( ΑριθμόςΑρχείου )
Περιγραφή
Κλείνει ένα ανοιχτό αρχείο. Εάν δεν υπάρχει ανοιχτό αρχείο με τον δοσμένο αριθμό αρχείου, η εντολή δεν εκτελείται. Στην περίπτωση που δεν προσδιοριστεί κάποιος αριθμός αρχείου θα χρησιμοποιηθεί ο αριθμός μηδέν (0).
Δες επίσης
Color
Σύνταξη
color ΌνομαΧρώματος
color ( ΌνομαΧρώματος )
color Τιμή rgb
color ( Τιμή rgb )
color ΧρώμαΣτυλού , ΧρώμαΠινέλου
color ( ΧρώμαΣτυλού , ΧρώμαΠινέλου )
color rgbΣτυλού , rgbΠινέλου
color ( rgbΣτυλού , rgbΠινέλου )
Περιγραφή
Θέτει το τρέχον χρώμα σχεδίασης ως ΌνομαΧρώματος ή μια τιμή ARGB όπου ( (a * 256 + r) * 256 + b) * 256 + g. Εάν δοθεί ένα χρώμα μόνο τότε το ίδιο θα χρησιμοποιηθεί και για τον στυλό και για το πινέλο.
Όταν σχεδιάζονται σχήματα (Τόξο,Κύκλος,Πίτα,Πολύγωνο,Ορθογώνιο, και Σφραγίδα), τα περιγράμματα των σχημάτων θα έχουν το χρώμα του στυλού και το εσωτερικό των σχημάτων το χρώμα του πινέλου. Το πινέλο με την τιμή CLEAR χρησιμοποιείται για να σχεδιαστούν μόνο τα περιγράμματα.
Εάν έχουν και ο στυλός και το πινέλο την τιμή CLEAR τότε τα σχεδιαζόμενα εικονοστοιχεία ή σχήματα θα σβήνουν τα ήδη υπάρχοντα γραφικά. Αυτό είναι εξαιρετικά χρήσιμο όταν δημιουργούνται sprites με χρήση της εντολής Spriteslice.
| Ονόματα χρωμάτων και τιμές RGB | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Όνομα χρώματος | Τιμή ARGB | Αναπαράσταση ως ακέραιος | |
| black | 255, 0, 0, 0 | 4278190080 | <hi #000000>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| white | 255, 255, 255, 255 | 4294506744 | <hi #FFFFFF>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| red | 255, 255, 0, 0 | 4294901760 | <hi #FF0000>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| darkred | 255, 128, 0, 0 | 4286578688 | <hi #800000>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| green | 255, 0, 255, 0 | 4278255360 | <hi #00FF00>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| darkgreen | 255, 0, 128, 0 | 4278222848 | <hi #008000>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| blue | 255, 0, 0, 255 | 4278190335 | <hi #0000FF>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| darkblue | 255, 0, 0, 128 | 4278190208 | <hi #000080>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| cyan | 255, 0, 255, 255 | 4278255615 | <hi #00FFFF>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| darkcyan | 255, 0, 128, 128 | 4278222976 | <hi #008080>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| purple | 255, 255, 0, 255 | 4294902015 | <hi #FF00FF>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| darkpurple | 255, 128, 0, 128 | 4286578816 | <hi #800080>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| yellow | 255, 255, 255, 0 | 4294967040 | <hi #FFFF00>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| darkyellow | 255, 128, 128 ,0 | 4286611456 | <hi #808000>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| orange | 255, 255, 102, 0 | 4294927872 | <hi #FF6600>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| darkorange | 255, 176, 61 ,0 | 4289344256 | <hi #B03D00>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| grey | 255, 164, 164 ,164 | 4288980132 | <hi #A4A4A4>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| darkgrey | 255, 128, 128 ,128 | 4286611584 | <hi #808080>~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~~~SP~~</hi> |
| clear | 0, 0, 0, 0 | 0 | ~~SP~~ |
Απαρχαιωμένη μορφή
Από την έκδοση 0.9.9.26 η σύνταξη “color red, blue, green” ή “color ( red, blue, green )” θεωρείται πεπαλαιωμένη και θα εμφανίζεται μια προειδοποίηση κάθε φορά που απαντάται στον κώδικα. Θα πρέπει να αντικαθίσταται με την σύνταξη “color rgb ( red, blue, green )”.
Δες επίσης
Παράδειγμα
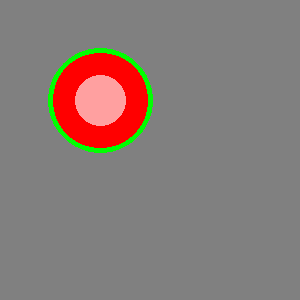
clg color rgb(128,128,128) rect 0,0,graphwidth, graphheight penwidth 5 color green,red circle 100,100,50 penwidth 1 color rgb(255,160,160) circle 100,100,25
Θα ζωγραφίσει ένα γκρι ορθογώνιο με έναν πράσινο κύκλο που εμπεριέχει έναν κόκκινο και έναν ροζ κύκλο.
Ιστορικό
0.9.5m - Προσθήκη σύνταξης “COLOR r,g,b” και αριθμητικής αναπαράστασης χρωμάτων
0.9.9.26 - Προσθήκη πινέλου και πεπαλαίωση της σύνταξης “COLOR r,g,b”.
0.9.9.28 - Τροποποίηση χρωματικών τιμών για συμπερίληψη τιμής Alpha (διαφάνεια) και μετατροπή χρωματικών σταθερών σε νέες τιμές ARGB.
0.9.9.45 - Μετατροπή τιμών σε θετικούς αριθμούς προς πιστή ακολούθηση του τύπου.
Cos
Format
cos ( expression )
Description
Computes the cosine of expression. Expression must be in radians.
Note
The cos function does not produce an exact result.
See Also
Example
Currentdir
Σύνταξη
currentdir
currentdir ( )
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει την πλήρη διαδρομή αρχείου του φακέλου όπου είναι εγκατεστημένη η ΒASIC-256. Σε όλα τα λειτουργικά συστήματα (συμπεριλαμβανομένων των Windows) μια δεξιά κάθετος (/) διαχωρίζει τους φακέλους μιας διαδρομής.
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.6r
Day
Σύνταξη
day
day ( )
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει την τρέχουσα μέρα του μήνα (1-31), όπως είναι καταχωρημένη στο ρολόι του συστήματος.
Δες επίσης
Παράδειγμα
print "H simerini imerominia einai: "; print (month + 1) + "/" + day + "/" + year
θα απεικονίσει
H simerini imerominia einai: 11/30/2009
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.4
DBClose
Σύνταξη
dbclose
dbclose ( )
dbclose ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων
dbclose ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων )
Description
Κλείνει μια ανοιχτή βάση δεδομένων SQLite, αριθμημένη από το 0 έως το 7. Εάν παραλειφθεί ο αριθμός, τότε θα κλείσει την βάση δεδομένων #0.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή στην σελίδα DBOpen.
Δες επίσης
Εξωτερικοί σύνδεσμοι
Περισσότερες πληροφορίες σχετικά με τις βάσεις δεδομένων και την SQLite μπορείς να βρεις στις σελίδες SQLite Home Page και SQL στην Βικιπαίδεια.
Ιστορικό
0.9.6y - Εισαγωγή
0.9.9.19 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για μέχρι 8 βάσεις δεδομένων ανοιχτές ταυτόχρονα
DBCloseSet
Σύνταξη
dbcloseset
dbcloseset ( )
dbcloseset ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων
dbcloseset ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων )
dbcloseset ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΠίνακα
dbcloseset ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων, ΑριθμόςΠίνακα )
Περιγραφή
Κλείνει έναν πίνακα που ανοίχθηκε με την εντολή DBOpenSet.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή στην σελίδα DBOpen.
Δες επίσης
Εξωτερικοί σύνδεσμοι
Περισσότερες πληροφορίες σχετικά με τις βάσεις δεδομένων και την SQLite μπορείς να βρεις στις σελίδες SQLite Home Page και SQL στην Βικιπαίδεια.
Ιστορικό
0.9.6y - Εισαγωγή
0.9.9.19 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για μέχρι 8 βάσεις δεδομένων ανοιχτές ταυτόχρονα
DBExecute
Σύνταξη
dbexecute Εντολή Sql
dbexecute ( Εντολή Sql )
dbexecute ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , Εντολή Sql
dbexecute ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , Εντολή Sql )
Περιγραφή
Εκτελεί μια εντολή SQL στην ανοιγμένη βάση δεδομένων. Δεν δημιουργεί πίνακες.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή στην σελίδα DBOpen.
Δες επίσης
Εξωτερικοί σύνδεσμοι
Περισσότερες πληροφορίες σχετικά με τις βάσεις δεδομένων και την SQLite μπορείς να βρεις στις σελίδες SQLite Home Page και SQL στην Βικιπαίδεια.
Ιστορικό
0.9.6y - Εισαγωγή
0.9.9.19 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για μέχρι 8 βάσεις δεδομένων ανοιχτές ταυτόχρονα
DBFloat
Σύνταξη
dbfloat ( ΑριθμόςΣτήλης )
dbfloat ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΣτήλης )
dbfloat ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΠίνακα , ΑριθμόςΣτήλης )
dbfloat ( ΌνομαΣτήλης )
dbfloat ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΌνομαΣτήλης )
dbfloat ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΠίνακα , ΌνομαΣτήλης )
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει έναν δεκαδικό αριθμό από τον δοσμένο αριθμό ή όνομα στήλης της τρέχουσας σειράς του ανοιγμένου πίνακα. Εάν το πεδίο είναι κενό (τιμή NULL) τότε θα επιστραφεί ο αριθμός 0.0. Έλεγχος για NULL μπορεί να γίνει με χρήση της συνάρτησης DBNull.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή στην σελίδα DBOpen.
Δες επίσης
Εξωτερικοί σύνδεσμοι
Περισσότερες πληροφορίες σχετικά με τις βάσεις δεδομένων και την SQLite μπορείς να βρεις στις σελίδες SQLite Home Page και SQL στην Βικιπαίδεια.
Ιστορικό
0.9.6y - Εισαγωγή
0.9.9.19 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για μέχρι 8 βάσεις δεδομένων ανοιχτές ταυτόχρονα
0.9.9.22 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για χρήση ονόματος εκτός αριθμού
DBInt
Σύνταξη
dbint ( ΑριθμόςΣτήλης )
dbint ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΣτήλης )
dbint ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΠίνακα , ΑριθμόςΣτήλης )
dbint ( ΌνομαΣτήλης )
dbint ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΌνομαΣτήλης )
dbint ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΠίνακα , ΌνομαΣτήλης )
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει έναν ακέραιο αριθμό από τον δοσμένο αριθμό ή όνομα στήλης της τρέχουσας σειράς του ανοιγμένου πίνακα. Εάν το πεδίο είναι κενό (τιμή NULL) τότε θα επιστραφεί ο αριθμός 0. Έλεγχος για NULL μπορεί να γίνει με χρήση της συνάρτησης DBNull.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή στην σελίδα DBOpen.
Δες επίσης
Εξωτερικοί σύνδεσμοι
Περισσότερες πληροφορίες σχετικά με τις βάσεις δεδομένων και την SQLite μπορείς να βρεις στις σελίδες SQLite Home Page και SQL στην Βικιπαίδεια.
Ιστορικό
0.9.6y - Εισαγωγή
0.9.9.19 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για μέχρι 8 βάσεις δεδομένων ανοιχτές ταυτόχρονα
0.9.9.22 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για χρήση ονόματος εκτός αριθμού
DBOpen
Σύνταξη
dbopen ΑρχείοSQLite
dbopen ( ΑρχείοSQLite )
dbopen ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑρχείοSQLite
dbopen ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑρχείοSQLite )
Περιγραφή
Ανοίγει ένα αρχείο SQLite. Εάν το αρχείο δεν υπάρχει τότε αυτό δημιουργείται. Μέχρι 8 βάσεις δεδομένων μπορούν να είναι ανοιχτές ταυτόχρονα. Σε περίπτωση που παραλειφθεί ο αριθμός μιας βάσης δεδομένων τότε θα χρησιμοποιηθεί ο αριθμός 0.
Παράδειγμα
#Βάση δεδομένων foo - δημιουργία μιας βάσης δεδομένων, αρχικοποίηση ενός πίνακα και ανάγνωση δεδομένων # δημιουργία μιας νέας βάσης δεδομένων ή άνοιγμα μιας υπάρχουσας dbopen "dbtest.sqlite3" # διαγραφή παλιότερου πίνακα foo - ανίχνευση σφάλματος σε περίπτωση που η βάση δεδομένων είναι καινούργια onerror errortrap dbexecute "drop table foo;" offerror # δημιουργία νέου πίνακα και αρχικοποίηση dbexecute "create table foo (id integer, words text, value decimal);" dbexecute "insert into foo values (1,'one',3.14);" dbexecute "insert into foo values (2,'two',6.28);" dbexecute "insert into foo values (3,'three',9.43);" # άνοιγμα μιας εγγραφής και προσπέλαση των σειρών δεδομένων dbopenset "select * from foo order by words;" while dbrow() print dbint(0) + dbstring(1) + dbfloat(2) end while dbcloseset # κλείσιμο βάσης δεδομένων dbclose end errortrap: # αποδοχή σφάλματος - καμία ενέργεια - επιστροφή στην επόμενη εντολή return
θα απεικονίσει
1one3.14 3three9.43 2two6.28
Δες επίσης
Εξωτερικοί σύνδεσμοι
Περισσότερες πληροφορίες σχετικά με τις βάσεις δεδομένων και την SQLite μπορείς να βρεις στις σελίδες SQLite Home Page και SQL στην Βικιπαίδεια.
Ιστορικό
0.9.6y - Εισαγωγή
0.9.9.19 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για μέχρι 8 βάσεις δεδομένων ανοιχτές ταυτόχρονα
DBOpenset
Σύνταξη
dbopenset ΕντολήSql
dbopenset ( ΕντολήSql )
dbopenset ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΕντολήSql
dbopenset ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΕντολήSql )
dbopenset ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΠίνακα , ΕντολήSql
dbopenset ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΠίνακα , ΕντολήSql )
Περιγραφή
Εκτελεί μια εντολή SQL και δημιουργεί μια εγγραφή η οποία μπορεί να προσπελαστεί από το πρόγραμμα και να χρησιμοποιηθούν τα απότελέσματα.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή στην σελίδα DBOpen.
Δες επίσης
Εξωτερικοί σύνδεσμοι
Περισσότερες πληροφορίες σχετικά με τις βάσεις δεδομένων και την SQLite μπορείς να βρεις στις σελίδες SQLite Home Page και SQL στην Βικιπαίδεια.
Ιστορικό
0.9.6y - Εισαγωγή
0.9.9.19 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για μέχρι 8 βάσεις δεδομένων ανοιχτές ταυτόχρονα, κάθε μία με 8 πίνακες
DBRow
Σύνταξη
dbrow
dbrow ( )
dbrow ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων )
dbrow ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΠίνακα )
Περιγραφή
Μετάθεση στην επόμενη σειρά του πίνακα. Επιστρέφει true εάν υπάρχει σειρά ή false εάν είμαστε στο τέλος του πίνακα.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή στην σελίδα DBOpen.
Δες επίσης
Εξωτερικοί σύνδεσμοι
Περισσότερες πληροφορίες σχετικά με τις βάσεις δεδομένων και την SQLite μπορείς να βρεις στις σελίδες SQLite Home Page και SQL στην Βικιπαίδεια.
Ιστορικό
0.9.6y - Εισαγωγή
0.9.9.19 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για μέχρι 8 βάσεις δεδομένων ανοιχτές ταυτόχρονα, κάθε μία με 8 πίνακες
DBString
Σύνταξη
dbstring ( ΑριθμόςΣτήλης )
dbstring ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΣτήλης )
dbstring ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΠίνακα , ΑριθμόςΣτήλης )
dbstring ( ΌνομαΣτήλης )
dbstring ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΌνομαΣτήλης )
dbstring ( ΑριθμόςΒάσηςΔεδομένων , ΑριθμόςΠίνακα , ΌνομαΣτήλης )
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει μια συμβολοσειρά από το δοσμένο όνομα ή αριθμό στήλης της τρέχουσας σειράς του ανοιγμένου πίνακα. Εάν το πεδίο έχει τιμή NULL τότε θα επιστραφεί η κενή συμβολοσειρά “” . Έλεγχος για NULL μπορεί να γίνει με χρήση της συνάρτησης DBNull.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή στην σελίδα DBOpen.
Δες επίσης
Εξωτερικοί σύνδεσμοι
Περισσότερες πληροφορίες σχετικά με τις βάσεις δεδομένων και την SQLite μπορείς να βρεις στις σελίδες SQLite Home Page και SQL στην Βικιπαίδεια.
Ιστορικό
0.9.6y - Εισαγωγή
0.9.9.19 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για μέχρι 8 βάσεις δεδομένων ανοιχτές ταυτόχρονα, κάθε μία με 8 πίνακες
0.9.9.22 - Προσθήκη ικανότητας για χρήση ονόματος εκτός αριθμού
Degrees
Format
degrees ( expression )
Description
See Also
Dim
Σύνταξη
dim αριθμητικήΜεταβλητή ( ακέραιος )
dim αλφαριθμητικήΜεταβλητή$ ( ακέραιος )
dim αριθμητικήΜεταβλητή ( σειρές , στήλες )
dim αλφαριθμητικήΜεταβλητή$ ( σειρές , στήλες )
Περιγραφή
Δημιουργεί έναν νέο μονοδιάστατο πίνακα μήκους ακέραιος ή έναν δισδιάστατο που μπορεί να προσπελαστεί με την χρήση των σειρά και στήλη. Αναλόγως της χρησιμοποιούμενης μεταβλητής δημιουργείται ένας αλφαριθμητικός ή αριθμητικός πίνακας.
Το πρώτο στοιχείο ενός πίνακα έχει τον δείκτη 0 (μηδέν). Οι δείκτες έχουν τιμές από 0 έως (μήκος πίνακα)-1.
Δες επίσης
ArrayBase, ArrayLength, Assigned, Dim, Fill, Map, Redim, TypeOf, Unassign, VariableWatch
Παράδειγμα
dim z(5)
z = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
print z[0] + " " + z[4]
θα απεικονίσει
1 5
Παράδειγμα δεύτερο
dim c$(4)
c$ = {"cow", "brow", "how", "now"}
print c$[2] + " " + c$[3] + " ";
print c$[1] + " " + c$[0] + "?"
θα απεικονίσει
how now brown cow?
End
Format
end
Description
Halts program execution.
Example
print "I am done." end print "Or am I?"
will print
I am done.
See Also
Eof
Σύνταξη
eof
eof()
eof(ΑριθμόςΑρχείου)
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει true εάν έχουμε φτάσει στο τέλος του αρχείου και false εάν όχι. Στην περίπτωση που δεν έχει προσδιοριστεί αριθμός αρχείου θα χρησιμοποιηθεί ο αριθμός μηδέν (0).
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.4
Exists
Σύνταξη
exists ( ΔιαδρομήΑρχείου )
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει true εάν υπάρχει η δοσμένη διαδρομή αρχείου.
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.4
FastGraphics
Format
fastgraphics
Description
Turns fastgraphics mode on, until the program is halted. Fastgraphics mode means that the graphics display is not updated until a REFRESH command is issued. It can be used to significantly speed up complex animations and eliminate flicker.
Note
When doing animation, it's recommended to do all of your drawing commands in subroutines and use a single REFRESH command after all drawing has been done for that frame.
See Also
Float
Format
float ( expression )
Description
Convert expression to a floating point (decimal) number. Float will convert a string or an integer to a decimal value. If the expression can not be converted then a zero will be returned.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.4
Floor
Format
floor ( expression )
Description
Returns the greatest integer that is less than or equal to expression
See Also
Font
Format
font fontname, point, weight
Description
Sets the font used by the text command to fontname. Size is defined in points (1/72“) Weight represents a number from 1 to 100 that defines how dark the letters will be drawn. Light=25, Normal=50, and Bold=75.
Example
color grey rect 0,0,graphwidth,graphheight color red font "Times New Roman",18,50 text 10,100,"This is Times New Roman" color darkgreen font "Tahoma",28,100 text 10,200,"This is BOLD!"
See Also
New To Version
0.9.4
GetColor
Σύνταξη
getcolor
getcolor()
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει την τιμή ARGB του τρέχοντος χρώματος στυλού (που τέθηκε με την εντολή color). Η ARGB υπολογίζεται από τον τύπο ( (a * 256 + r) * 256 + b) * 256 + g όπου a, r, g, και b είναι τιμές μεταξύ 0 και 255. Εάν το χρώμα έχει οριστεί ως CLEAR τότε θα επιστραφεί 0.
Δες επίσης
Παράδειγμα
color red, blue print getcolor
θα απεικονίσει
-65536
Ιστορικό
0.9.5m - Εισαγωγή
0.9.9.28 - Τροποποίηση για επιστροφή τιμών ARGB
GetSlice
Format
getslice(x, y, width, height)
Description
Return a string that contains a Hexadecimal (base 16) representation of the rectangle defined by the parameters. String is formatted as first 4 bytes - width, next 4 bytes - height, 6 bytes for each pixel (width * height).
Example
color 16-1 plot 1,1 color 16^2-1 plot 1,2 color 16^3-1 plot 2,1 color 16^4-1 plot 2,2 print getslice(1, 1, 2, 2)
displays
0002000200000f000fff0000ff00ffff
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6b
Goto
Format
goto label
Description
Jumps to the specified label.
See Also
Example
print "I"; goto skipit print " don't"; skipit: # print " want cookies."
will print
I want cookies.
Notes
As of version 0.9.9.2 Goto, Gosub, and labels can not be used in Function and Subroutine definitions.
Graphheight
Format
graphheight
graphheight()
Description
Returns the height (y dimension) of the current graphics display window.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.3
Graphsize
Format
graphsize x_expression, y_expression
Description
Changes the size of the graphics display window and redraws the BASIC256 application.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.3
Graphwidth
Format
graphwidth
graphwidth()
Description
Returns the width (x dimension) of the current graphics display window.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.3
Hour
Σύνταξη
hour
hour()
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει την τρέχουσα ώρα της μέρας (0-23), όπως είναι καταχωρημένη στο ρολόι του συστήματος.
Παράδειγμα
# apeikonisi imerominias
dim months$(12)
months$ = {"January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"}
print year + "-" + months$[month] + "-" + right("0" + day, 2)
# apeikonisi wras
h = hour
if h > 12 then
h = h - 12
ampm$ = "PM"
else
ampm$ = "AM"
end if
if h = 0 then h = 12
print right("0" + h, 2) + "-" + right("0" + minute, 2) + "-" + right("0" + second, 2) + " " + ampm$
θα απεικονίσει κάτι παρόμοιο με.
2010-July-15 10-00-02 PM
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.4
Instr
Format
instr ( haystack , needle )
instr ( haystack , needle , start )
instr ( haystack , needle , start , caseinsensitive)
Description
Check to see if the string needle is contained in the string haystack. If it is, then this function will return the index of starting character of the first place where needle occurs. Otherwise, this function will return 0. You may also specify an optional starting location for the search to begin start and a boolean value caseinsensitive to specify that the search will treat upper and lower case letters the same.
Note
String indices begin at 1.
Example
print instr("Hello", "lo")
print instr("101,222,333",",",5)
will display
4 8
Version
0.9.6.55
Int
Format
int ( expression )
Description
Convert expression to an integer (whole) number. Int will convert a string or a float to an integer value. If the expression can not be converted then a zero will be returned.
See Also
Imgload
Format
imgload x, y, filename
imgload x, y, scale, filename
imgload x, y, scale, rotation, filename
Description
Load an image or picture from a file and paint it on the Graphics Output Window.
The parameters x and y represent the location on the screen for the CENTER of the loaded image. This behaviour is different than all of the other graphics statements. The axis of rotation will also be this CENTER point.\\The Imgload starement will read in most common image file formats including: BMP (Windows Bitmap), GIF (Graphic Interchange Format),JPG/JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group), and PNG (Portable Network Graphics).
Optionally scales size of the loaded image by the defined scale (1=normal size). Also optionally rotates the image by a specified angle around the images center (clockwise in radians).
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6l
Input
Format
input prompt_expression, stringvariable
input prompt_expression, numericvariable
input stringvariable
input numericvarvariable
input prompt_expression, string_array_variable[index]
input prompt_expression, numeric_array_variable[index]
input string_array_variable[index]
input numeric_array_variable[index]
input prompt_expression, string_array_variable[index, index]
input prompt_expression, numeric_array_variable[index, index]
input string_array_variable[index, index]
input numeric_array_variable[index, index]
Description
Waits for the user to type a line of text into the text output window. When the user hits the enter or return key, the line is read in to stringvar or numericvariable.
User may optionally be prompted for the input by expression.
If a numeric variable is specified and non-numeric data is entered a zero will be assigned to the numeric variable.
References to array elements may also be specified.
Key
Format
key
key()
Description
Immediately returns an integer value corresponding to the currently pressed keyboard key. If no key has been pressed since the last call to the key function then the number zero (0) will be returned. This function returns the code for the key pressed not always the ASCII value of the character.
Note
if key = 47 then print key
will not display the desired results, because it's calling key twice in succession, and will return different values each time. This code will do what you want:
a = key if a = 47 then print a
Partial List of Keys
| ESC=16777216 | Space=32 | ||||||
| 0=48 | 1=49 | 2=50 | 3=51 | 4=52 | 5=53 | 6=54 | 7=55 |
| 8=56 | 9=57 | ||||||
| A=65 | B=66 | C=67 | D=68 | E=69 | F=70 | G=71 | H=72 |
| I=73 | J=74 | K=75 | L=76 | M=77 | N=78 | O=79 | P=80 |
| Q=81 | R=82 | S=83 | T=84 | U=85 | V=86 | W=87 | X=88 |
| Y=89 | Z=90 | ||||||
| Down Arrow=16777237 | Up Arrow=16777235 | Left Arrow=16777234 | Right Arrow=16777236 | ||||
Example
#press any keys loop: pause 1 a = key print a+" "+chr(a) goto loop
LastError
Σύνταξη
lasterror
lasterror ( )
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει τον κωδικό του τελευταίου σφάλματος εκτέλεσης.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορεί να χρησιμοποιηθεί η εντολή στην σελίδα Κωδικοί σφαλμάτων εκτέλεσης.
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.6z
LastErrorExtra
Σύνταξη
lasterrorextra
lasterrorextra ( )
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει επιπρόσθετες πληροφορίες σχετικά με το τελευταίο σφάλμα.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορεί να χρησιμοποιηθεί η εντολή στην σελίδα Κωδικοί σφαλμάτων εκτέλεσης.
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.6z
LastErrorLine
Σύνταξη
lasterrorline
lasterrorline ( )
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει τον αριθμό της σειράς του προγράμματος, στην οποία συνέβη το σφάλμα εκτέλεσης.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορεί να χρησιμοποιηθεί η εντολή στην σελίδα Κωδικοί σφαλμάτων εκτέλεσης.
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.6z
Left
Format
left( string, length)
Description
Returns a portion of the specified string, starting from the first character on the left and continuing for length characters.
See Also
Example
print left("Hello", 2)
will display
He
New To Version
0.9.5b
Length
Format
length( string )
Description
Returns the number of characters in string
Line
Σύνταξη
line x0, y0, x1, y1
line(x0, y0, x1, y1)
Περιγραφή
Σχεδιάζει μια γραμμή από το σημείο x0,y0 στο σημείο x1, y1 με το τρέχον χρώμα στυλού. Το πάχος της γραμμής μπορεί να ρυθμιστεί με χρήση της εντολής PenWidth.
Παράδειγμα
clg color black line 50,50,200,200 penwidth 5 line 100,200,200,200 penwidth 10 line 100,200,50,50
Δες επίσης
Log
Format
log ( expression )
Description
Return the base e lograthim of expression.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.5w
Lower
Format
lower( string)
Description
Returns string with all alphabetic characters converted to lower case.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.5e
Mid
Format
mid( string, start character, length)
Description
Returns a portion of the specified string, starting from the start character, and continuing for length characters.
See Also
Example
print mid("Hello", 2, 3)
will display
ell
Minute
Σύνταξη
minute
minute()
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει το τρέχων λεπτό της ώρας(0-59), όπως είναι καταχωρημένο στο ρολόι του συστήματος.
Παράδειγμα
# apeikonisi imerominias
dim months$(12)
months$ = {"January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"}
print year + "-" + months$[month] + "-" + right("0" + day, 2)
# apeikonisi wras
h = hour
if h > 12 then
h = h - 12
ampm$ = "PM"
else
ampm$ = "AM"
end if
if h = 0 then h = 12
print right("0" + h, 2) + "-" + right("0" + minute, 2) + "-" + right("0" + second, 2) + " " + ampm$
θα απεικονίσει κάτι παρόμοιο με.
2010-July-15 10-00-02 PM
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.4
Month
Σύνταξη
month
month()
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει τον τρέχοντα μήνα, όπως είναι καταχωρημένος στο ρολόι του συστήματος. Ο Ιανουάριος είναι 0, ο Φεβρουάριος είναι 1… ο Δεκέμβριος είναι 11.
Παράδειγμα
cls
dim n$(12)
n$ = {"Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr", "May", "Jun", "Jul", "Aug", "Sep", "Oct", "Nov", "Dec"}
print day + "-" + n$[month] + "-" + year
την Πρωτοχρονιά θα απεικονίσει
1-Jan-2010
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.4
Mouseb
Format
mouseb
mouseb()
Description
Returns the buttons that currently pressed on the mouse (if over the graphic output). Returns 0 if no click has been recorded. If multiple buttons have been pressed the value is the sum of the values for all pressed buttons.
| Return Values | |
|---|---|
| Value | Mouse Button Pressed |
| 0 | None |
| 1 | Left |
| 2 | Right |
| 3 | Right and Left |
| 4 | Center |
See Also
New To Version
0.9.4d
Mousex
Format
mousex
mousex()
Description
Returns the current or last mouse x location of the mouse pointer over the graphic output.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.4d
Mousey
Format
mousey
mousey()
Description
Returns the current or last mouse y location of the mouse pointer over the graphic output.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.4d
NetClose
Format
netclose
netclose ( )
netclose socket_number
netclose ( socket_number )
Description
Close the specified network connection (socket). If socket_number is not specified socket number zero (0) will be used.
Example
See example of usage on NetConnect page.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6.31
NetConnect
Format
netconnect server_name, port_number
netconnect ( server_name, port_number )
netconnect socket_number, server_name, port_number
netconnect ( socket_number, server_name, port_number )
Description
Open a network connection (client) to a server. The IP address or host name of a server are specified in the server_name argument, and the specific network port number in the port_number argument. If socket_number is not specified socket number zero (0) will be used.
Example
Open two instances of BASIC-256 on a single computer. Paste the “server” code into one and the “client” code into the other. Run the server first and the client second. You can see how the messages are sent back and forth between the two different processes.
Server Code
# get a message and send back success
print "wait for connection on " + netaddress()
netlisten 9997
print "got connection"
do
while not netdata
pause .1
print ".";
end while
n$ = netread
print n$
netwrite "I got '" + n$ + "'."
until n$ = "end"
netclose
will display (where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IPv4 address of your computer)
wait for connection on xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx got connection .1 Hi There ....2 Hi There ........3 Hi There ..........4 Hi There .....5 Hi There .......6 Hi There ....7 Hi There ..........8 Hi There ....9 Hi There .....10 Hi There .end
Client Code
# have the user enter a message and send it to the server input "enter message?", m$ netconnect "127.0.0.1", 9997 for t = 1 to 10 pause rand netwrite t + " " + m$ print netread next t netwrite "end" print netread netclose
will display
enter message?Hi There I got '1 Hi There'. I got '2 Hi There'. I got '3 Hi There'. I got '4 Hi There'. I got '5 Hi There'. I got '6 Hi There'. I got '7 Hi There'. I got '8 Hi There'. I got '9 Hi There'. I got '10 Hi There'. I got 'end'.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6.31
NetData
Format
netdata
netdata ( )
netdata socket_number
netdata ( socket_number )
Description
Returns a true value (1) of there is data waiting to be read in using the NetRead function, else returns false (0). If socket_number is not specified socket number zero (0) will be used.
Example
See example of usage on NetConnect page.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6.31
NetListen
Format
netlisten port_number
netlisten ( port_number)
netlisten socket_number, port_number
netlisten ( socket_number, port_number)
Description
Open up a network connection (server) on a specific port address and wait for another program to connect. If socket_number is not specified socket number zero (0) will be used.
Example
See example of usage on NetConnect page.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6.31
NetRead
Format
netread
netread ( )
netread ( socket_number )
Description
Read data from the specified network connection and return it as a string. This function will wait until data is received. If socket_number is not specified socket number zero (0) will be used.
Example
See example of usage on NetConnect page.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6.31
NetWrite
Format
netwrite string
netwrite ( string )
netwrite socket_number, string
netwrite ( socket_number, string )
Description
Send a string to the specified open network connection. If socket_number is not specified socket number zero (0) will be used.
Example
See example of usage on NetConnect page.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6.31
Open and Openb
Σύνταξη
open ΌνομαΑρχείου
open(ΌνομαΑρχείου)
open ΑριθμόςΑρχείου, ΌνομαΑρχείου
open(ΑριθμόςΑρχείου, ΌνομαΑρχείου)
openb ΌνομαΑρχείου
openb(ΌνομαΑρχείου)
openb ΑριθμόςΑρχείου, ΌνομαΑρχείου
openb(ΑριθμόςΑρχείου, ΌνομαΑρχείου)
Περιγραφή
Ανοίγει ένα αρχείο για ανάγνωση και εγγραφή. Το όνομα αρχείου δίδεται ως συμβολοσειρά, και μπορεί να είναι μια πλήρης ή σχετική διαδρομή. Εάν δεν προσδιορισθεί αριθμός αρχείου τότε θα χρησιμοποιηθεί ο αριθμός μηδέν (0).
Η Openb ανοίγει τo αρχείο ως σύνολο δυαδικών αριθμών. Αυτός ο τρόπος ανοίγματος αρχείου συνίσταται για τα αρχεία που χρησιμοποιούν τις εντολές Readbyte και Writebyte.
Σημείωση
Η BASIC256 επιτρέπει την ύπαρξη μέχρι 8 ανοιχτών αρχείων ταυτόχρονα. Τα αρχεία αριθμούνται από το 0 έως το 7. Το άνοιγμα ενός αρχείου με αριθμό ενός ήδη ανοιχτού αρχείου θα οδηγήσει στο κλείσιμο του τελευταίου.
Δες επίσης
OffError
Σύνταξη
offerror
Περιγραφή
Απενεργοποιεί τον τελευταίο ανιχνευτή σφαλμάτων που ορίστηκε με την εντολή OnError. Στην περίπτωση που ολοι οι ανιχνευτές είναι απενεργοποιημένοι, τότε η ανίχνευση σφαλμάτων λειτουργεί με την προκαθορισμένη συμπεριφορά.
Δεν μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή OnError μέσα στην δομή Try / Catch / End Try.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή στην σελίδα Κωδικοί σφαλμάτων εκτέλεσης.
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.6z
OnError
Σύνταξη
onerror ετικέτα
Περιγραφή
Μεταφέρει την ροή του προγράμματος στην ετικέτα ή καλεί μια Subroutine όταν συμβεί ένα σφάλμα εκτέλεσης. Η επιστροφή στο σημείο όπου κλήθηκε η υπορουτίνα γίνεται με την εντολή Return. Οι ανιχνευτές σφαλμάτων καταχωρούνται σε μια στοίβα, έτσι ο τελευταίος ανιχνευτής, που δεν έχει απενεργοποιηθεί με την εντολή OffError, θα είναι και ο ενεργός.
Δεν μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή OnError μέσα σε μια δομή Try / Catch / End Try.
Παράδειγμα
Δες πως μπορείς να χρησιμοποιήσεις την εντολή στις σελίδες Κωδικοί σφαλμάτων εκτέλεσης και ThrowError.
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.6z
Pause
Format
pause seconds
pause (seconds)
Description
Halts execution for the specified number of seconds. The seconds value may be a decimal value, so sub-second precision is possible.
See Also
Pixel
Format
pixel (x, y )
Description
Returns the RGB value of the pixel at the x and y coordinate. If the pixels has not been set since the last Clg command or was drawn with the color CLEAR a -1 will be returned.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.5m
Plot
Σύνταξη
plot x, y
plot ( x, y )
Περιγραφή
Αλλάζει το εικονοστοιχείο με τις συντεταγμένες x,y στο τρέχον χρώμα.
Δες επίσης
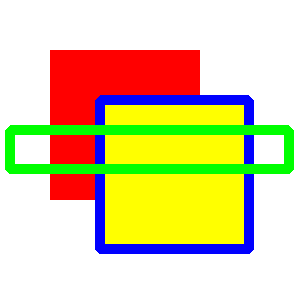
Poly
Σύνταξη
poly αριθμητικόςΠίνακας
poly {x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3 …}
Περιγραφή
Σχεδιάζει ένα πολύγωνο. Οι πλευρές του πολυγώνου καθορίζονται από τις τιμές που είναι αποθηκευμένες στον πίνακα, οι οποίες πρέπει να είναι ζεύγη συντεταγμένων και τοποθετημένα σειριακά. Ο αριθμός των γωνιών είναι ίσος με μέγεθοςΠίνακα/2. Ένα πολύγωνο μπορεί επίσης να προσδιορισθεί χρησιμοποιώντας έναν Ακαθόριστο πίνακα (μια λίστα ζευγών συντεταγμένων κλεισμένων σε άγκιστρα {}).
Σημείωση
Ο αριθμός των γωνιών στην σύνταξη με τον πίνακα αφαιρέθηκε στην έκδοση 0.9.4.
Δες επίσης
Παράδειγμα
# xrhsh pinaka
color blue
rect 0,0,300,300
color green
dim tri(1)
tri = {100, 100, 200, 200, 100, 200}
poly tri
# xrhsh akathoristou pinaka
color blue
rect 0,0,300,300
color green
poly {100, 100, 200, 200, 100, 200}
Και τα δύο προγράμματα χρησιμοποιούν την εντολή poly για να απεικονίσουν:
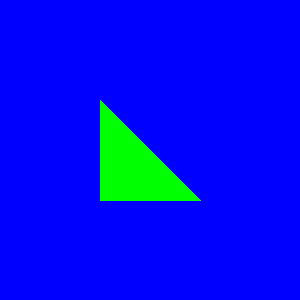
Δες επίσης
Σύνταξη
print έκφραση [ ; ]
Περιγραφή
Μεταβαίνει σε μια καινούργια σειρά και γράφει κείμενο στο παράθυρο κειμένου. Εάν υπάρχει το ερωτηματικό, τότε παραμένει στην ίδια σειρά.
Δες επίσης
PutSlice
Format
putslice x, y, slice$
putslice x, y, slice$, transparent color
Description
Put the graphics stored in the slice string on the screen at x,y. If a transparent color is specified then do not plot points of that color in the slice.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6b
Radians
Format
radians ( expression )
Description
See Also
Rand
Format
rand
rand()
Description
Returns a random number between 0 and 1. The distribution of the values is uniform.
Note
To produce random numbers between other values, simple multiply or add the appropriate numbers. For example, to generate an integer between 0 and 10, use int(rand * 10).
Read
Σύνταξη
read
read()
read(ΑριθμόςΑρχείου)
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει ένα λήμμα από ένα ανοιχτό αρχείο. Λήμμα είναι μια σειρά χαρακτήρων που διαχωρίζεται με ένα κενό, στήλη ή χαρακτήρα αλλαγής γραμμής. Εάν δεν προσδιορισθεί αριθμός αρχείου τότε θα χρησιμοποιηθεί ο αριθμός μηδέν (0).
Δες επίσης
Readline
Σύνταξη
readline
readline()
readline(ΑριθμόςΑρχείου)
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει μια ολόκληρη σειρά από ένα ανοιχτό αρχείο. Εάν δεν προσδιορισθεί αριθμός αρχείου τότε θα χρησιμοποιηθεί ο αριθμός μηδέν (0).
Δες επίσης
Rect
Σύνταξη
rect x,y,πλάτος,ύψος
rect ( x, y, πλάτος, ύψος )
Περιγραφή
Σχεδιάζει ένα ύψος x πλάτος ορθογώνιο χρησιμοποιώντας τα τρέχοντα χρώματα στυλού και πινέλου. Η πάνω αριστερή γωνία έχει τις συντεταγένες x,y.
Παράδειγμα
clg color red rect 50,50,150,150 penwidth 10 color blue, yellow rect 100,100,150,150 color green, clear rect 10,130,280,40
Δες επίσης
Redim
Σύνταξη
redim αριθμητικήΜεταβλητή( ακέραιος )
redim αλφαριθμητικήΜεταβλητή$( ακέραιος )
redim αριθμητικήΜεταβλητή( σειρές , στήλες )
redim αλφαριθμητικήΜεταβλητή$( σειρές , στήλες )
Περιγραφή
Αναμεγεθύνει έναν ήδη υπάρχων πίνακα, διατηρώντας ταυτόχρονα τα στοιχεία του. Εάν ένας πίνακας μεγαλώσει, τότε τα νέα στοιχεία θα αρχικοποιηθούν με μηδέν ή κενή συμβολοσειρά. Εάν αντίθετα μικρύνει, τότε τα στοιχεία που αποκόβονται στο τέλος θα χαθούν.
Δες επίσης
ArrayBase, ArrayLength, Assigned, Dim, Fill, Map, Redim, TypeOf, Unassign, VariableWatch
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.5t
Refresh
Format
refresh
Description
Updates the graphics output window to show all drawing since the previous refresh command. Refresh only works in Fastgraphics mode
See Also
Rem
Format
rem comment
# comment
Description
Line comment. A line beginning with REM (or the shortened #) is ignored.
See Also
Reset
Σύνταξη
reset
reset()
reset(ΑριθμόςΑρχείου)
Περιγραφή
Κενοποιεί ένα ανοιχτό αρχείο. Όλα τα δεδομένα που εμπεριέχονται χάνονται. Εάν δεν προσδιορισθεί αριθμός αρχείου τότε θα χρησιμοποιηθεί ο αριθμός μηδέν (0).
Δες επίσης
Rgb
Σύνταξη
rgb(κόκκινο, πράσινο, μπλε )
rgb(κόκκινο, πράσινο, μπλε, διαφάνεια )
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει την τιμή ARGB του χρώματος που αποτελείται από τις δοσμένες τιμές κόκκινου, πράσινου, και μπλε. Οι επιτρεπόμενες τιμές για το κόκκινο, πράσινο, μπλε και διαφάνεια είναι από 0 μέχρι 255. Εάν δεν προσδιοριστεί διαφάνεια τότε θα χρησιμοποιηθεί η τιμή 255 καθιστώντας το χρώμα αδιαφανές.
Δες επίσης
Ιστορικό
0.9.5m - Εισαγωγή
0.9.9.28 - Προσθήκη τιμής alpha (διαφάνεια)
Right
Format
right( string, length)
Description
Returns a portion of the specified string, starting from the last length characters from the right end of the of the string.
See Also
Example
print right("Hello", 2)
will display
lo
New To Version
0.9.5b
Say
Format
say expression
say ( expression )
Description
Uses the the system Text to Speech (TTS) engine to say the expression. In LINUX the FLite or eSpeak libraries are required. In Windows the current default SAPI voice will be used.
Notes
Windows SAPI will use the default voice you have defined on your control panel. To change the default for Linux/Mac using the ESpeak library you need to copy the desired voice file to the name default.
# Statements to set default language to 'fr' on Ubuntu 10.10 # Your system may be different cd /usr/share/espeak-data/voices sudo cp fr default
New To Version
0.9.4
Second
Σύνταξη
second
second()
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει το τρέχων δευτερόλεπτο (0-59), όπως είναι καταχωρημένο στο ρολόι του συστήματος.
Παράδειγμα
# apeikonisi imerominias
dim months$(12)
months$ = {"January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"}
print year + "-" + months$[month] + "-" + right("0" + day, 2)
# apeikonisi wras
h = hour
if h > 12 then
h = h - 12
ampm$ = "PM"
else
ampm$ = "AM"
end if
if h = 0 then h = 12
print right("0" + h, 2) + "-" + right("0" + minute, 2) + "-" + right("0" + second, 2) + " " + ampm$
θα απεικονίσει κάτι παρόμοιο με.
2010-July-15 10-00-02 PM
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.4
Seek
Σύνταξη
seek Θέση
seek ( Θέση )
seek ΑριθμόςΑρχείου, Θέση
seek ( ΑριθμόςΑρχείου, Θέση )
Περιγραφή
Καθορίζει την θέση εγγραφής/ανάγνωσης, η οποία είναι δοσμένη ως μετατόπιση σε bytes από την αρχή του αρχείου. Εάν δεν προσδιορισθεί αριθμός αρχείου τότε θα χρησιμοποιηθεί ο αριθμός μηδέν (0).
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.4
Sin
Format
sin ( expression )
Description
Computes the sine of expression. Expression must be in radians.
Note
The sin function does not produce an exact result.
See Also
Example
Size
Σύνταξη
size
size()
size(ΑριθμόςΑρχείου)
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει σε bytes το μέγεθος ενός ανοιχτού αρχείου. Εάν δεν προσδιορισθεί αριθμός αρχείου τότε θα χρησιμοποιηθεί ο αριθμός μηδέν (0).
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.4
Sound
Format
sound frequency, duration
sound ( frequency, duration )
sound ( array )
sound array
sound {frequency1, duration1, frequency2, duration2, …}
Description
Play a sound from the computer's speakers.Frequency is expressed in Hz and duration is expressed in milliseconds (1000 in a second). An array or list containing frequency and durations may also be passed. This eliminates any clicking between sounds when more than one is being output sequentially. Sound support for LINUX systems was added in version 0.9.5g. Sound was changed to use the default sound device in Windows in version 0.9.5h
See Also
Spritecollide
Format
spritecollide ( sprite1, sprite2)
Description
Function returns true if the two sprites are colliding. The Spritecollide function assumes that the sprites are bounded by a rectangle the size of the loaded image. Collision is calculated by using these rectangles. For round or oddly shaped sprites this function may over detect collision.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6n
Spritedim
Format
spritedim n
spritedim ( n )
Description
Create n sprite placeholders in memory. Sprites are accessed in your program by a sprite number from 0 to n-1.
Example
# creates a sprite with number 0 clg fastgraphics spritedim 1 a$="Basic 256" Text 0,0,a$ spriteslice 0,0,0,textwidth (a$),textheight() spriteshow 0 # rotates and enlarges sprite for n=0 to 2*pi step .002 clg spriteplace 0,150,150,n,n refresh next n
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6n
Spriteh
Format
spriteh ( spritenumber )
Description
Returns the height, in pixels, of a loaded sprite.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6n
Spritehide
Format
spritehide spritenumber spritehide ( spritenumber )
Description
Hides a sprite. All image and position information is retained.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6n
Spriteload
Format
spriteload spritenumber, filename
spriteload ( spritenumber, filename )
Description
Load an image or picture from a file and save it as a sprite. The sprite will be active and movable but will not display on the screen until the Spriteshow statement is executed for that sprite.\\The Spriteload statement will read in most common image file formats including: BMP (Windows Bitmap), GIF (Graphic Interchange Format),JPG/JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group), and PNG (Portable Network Graphics).
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6n
Spritemove
Format
spritemove spritenumber, dx, dy
spritemove ( spritenumber, dx, dy )
spritemove spritenumber, x, y, s
spritemove ( spritenumber, x, y, s )
spritemove spritenumber, x, y, s, r
spritemove ( spritenumber, x, y, s, r )
Description
Move a sprite from its current position by the specified number of pixels. Motion will be limited to the current screen. Optionally the sprite may be rotated or scaled by defining optional the r and s parameters. The degree r is measured in radians. Rotation and scaling are relative to the previous state of the sprite.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6n
Rotate and scale new to 0.9.9.15
Spriteplace
Format
spriteplace spritenumber, x, y
spriteplace ( spritenumber, x, y )
spriteplace spritenumber, x, y, s
spriteplace ( spritenumber, x, y, s )
spriteplace spritenumber, x, y, s, r
spriteplace ( spritenumber, x, y, s, r )
Description
Place the center of a sprite at a specific location on the screen (x,y). Like Imgload sprite positioning is relative to the center of the sprite and not the top left corner as with most other graphical statements.
Optionally the sprite may be rotated or scaled by defining optional the r and s parameters. The degree r is measured in radians.
Example
See Spritedim
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6n
rotate and scale 0.9.9.15
Spriteshow
Format
spriteshow spritenumber
spriteshow ( spritenumber )
Description
Show a hidden sprite.
Example
See Spritedim
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6n
Spriteslice
Format
spriteslice spritenumber, x, y, width, height
spriteslice ( spritenumber, x, y, width, height )
Description
Copy the rectangular region of the screen with it's top left corner represented by x and y of the specified height and width and create a sprite. The sprite will be active and movable but will not be visible until the Spriteshow statement is executed. It is recommended that you execute the Clg command before drawing and slicing the sprite. All unpainted pixels will be transparent when the sprite is drawn on the screen. Transparent pixels may also be set by drawing with the color CLEAR.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6o
Spritev
Format
spritev ( spritenumber )
Description
Returns true if the sprite is visible.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6o
Spritew
Format
spritew ( spritenumber )
Description
Returns the width, in pixels, of a loaded sprite.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6n
Spritex
Format
spritex ( spritenumber )
Description
Returns the x coordinate of the center of a loaded sprite.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6n
Spritey
Format
spritey ( spritenumber )
Description
Returns the y coordinate of the center of a loaded sprite.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.6n
Stamp
Format
stamp x, y, array
stamp x, y, {x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3 …}
stamp x, y, scale, array
stamp x, y, scale, {x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3 …}
stamp x, y, scale, rotation, array
stamp x, y, scale, rotation, {x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3 …}
Description
Draws a polygon with top left corner (origin) at x, y. Optionally scales size of polygon by the defined scale (1=normal size). Also optionally rotates the polygon by a specified angle around the origin (clockwise in radians). The vertices of the polygon are defined by the values in an array, which should be stored as x,y pairs, sequentially. The length of the array/2 will define the number of points. A stamped polygon can also be specified using a list of x,y pairs enclosed in curly braces {}.
See Also
Example
Both of the code blocks below will draw a pair of green triangles on the graphics window:
clg
color blue
rect 0,0,300,300
color green
dim tri(6)
tri = {0, 0, 100, 100, 0, 100}
# stamp the triangle at 0,0 (full size)
stamp 100, 100, tri
# stamp the triangle at 200,100 (half size)
stamp 200, 100, .5, tri
clg
color blue
rect 0,0,300,300
color green
# stamp the triangle at 0,0 (full size)
stamp 100, 100, {0, 0, 100, 100, 0, 100}
# stamp the triangle at 200,100 (half size)
stamp 200, 100, .5, {0, 0, 100, 100, 0, 100}
New To Version
0.9.4
See Also
String
Format
string ( expression )
Description
Returns the string representation of a number.
Example
number = 30+2 print string(number)
Results with
32
See Also
System
Format
system expression
system ( expression )
Description
Execute a system command in a terminal window. WARNING: This can be a very dangerous statement. Only use it if you know what you are doing.
This statement may be disabled because of potential system security issues. Availability may be configured in the IDE by going to the Edit>Preferences menu.
Example
system("BASIC256 -r HelloWorld.kbs")
Brings up the program without its source code visible and runs it.
New To Version
0.9.5h
Tan
Format
tan ( expression )
Description
Computes the tangent of expression. Expression must be in radians.
Note
The tan function does not produce an exact result.
See Also
Example
Text
Format
text x, y, string
text ( x, y, string )
Description
Paints a text string on the Graphics Output Window at x, y using the current color and font.
Example
color grey rect 0,0,graphwidth,graphheight color red font "Times New Roman",18,50 text 10,100,"This is Times New Roman" color darkgreen font "Tahoma",28,100 text 10,200,"This is BOLD!"
See Also
New To Version
0.9.4
Upper
Format
upper ( string )
Description
Returns string with all alphabetic characters converted to upper case.
See Also
Example
print upper("BlUe!")
will display
BLUE!
New To Version
0.9.5e
Volume
Format
volume level
volume ( level )
Description
Adjust the volume of the notes played with the Sound command. Volume levels must be numeric values from 0 to 10. The default volume is 5.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.5i
WAVplay
Format
wavplay filename
wavplay ( filename )
Description
Play WAV audio file asynchronously (in the background).
See Also
New To Version
0.9.4
WAVstop
Format
wavstop
Description
Stop playing the current asynchronous (background) WAV audio file.
See Also
New To Version
0.9.4
Write
Σύνταξη
write Συμβολοσειρά
write ( Συμβολοσειρά )
write ΑριθμόςΑρχείου, Συμβολοσειρά
write ( ΑριθμόςΑρχείου, Συμβολοσειρά )
Περιγραφή
Γράφει την δοσμένη συμβολοσειρά στο τέλος ενός ανοιχτού αρχείου. Εάν δεν προσδιορισθεί αριθμός αρχείου τότε θα χρησιμοποιηθεί ο αριθμός μηδέν (0).
Δες επίσης
Writeline
Σύνταξη
writeline Συμβολοσειρά
writeline ( Συμβολοσειρά )
writeline ΑριθμόςΑρχείου, Συμβολοσειρά
writeline ( ΑριθμόςΑρχείου, Συμβολοσειρά )
Περιγραφή
Γράφει την δοσμένη συμβολοσειρά με έναν επιθημένο χαρακτήρα αλλαγής γραμμής στο τέλος ενός ανοιχτού αρχείου. Εάν δεν προσδιορισθεί αριθμός αρχείου τότε θα χρησιμοποιηθεί ο αριθμός μηδέν (0).
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.4
Year
Σύνταξη
year
year ( )
Περιγραφή
Επιστρέφει το τρέχων 4-ψήφιο έτος, όπως είναι καταχωρημένο στο ρολόι του συστήματος.
Παράδειγμα
print "H simerini imerominia einai "; print (month + 1) + "/" + day + "/" + year
θα απεικονίσει
H simerini imerominia einai 11/30/2009
Δες επίσης
Εισήχθηκε με την έκδοση
0.9.4